Factors to Consider When Choosing a Laptop Screen: Resolution, Color Gamut, and MORE
Step. 1 Decide on the size and the resolution of the screen
The image shown on a monitor is composed of a square color grid, which is called “pixel”. More pixels in the fixed-size screen provide more-detailed representations of the original image. The “resolution” refers to the number of horizontal and vertical pixels on the screen. The commonly heard terms – “Full HD” and “4K UHD” refer to different resolution definitions. The higher the resolution, the clearer and more refined the image quality.
In terms of specifications, Full HD is characterized by a screen with 1,920 horizontal pixels and 1,080 vertical pixels (1920X1080). The resolution of 4K UHD is 4 times that of FHD, reaching an ultra-high resolution of 3840X2160. A 4K resolution screen display offers a clearer, sharper image for showing videos and photos with higher source resolution.

Step 2. Choose the panel that best suits your needs
Why do some screen displays achieve better looking images compared to others of the same resolution? Aside from resolution, different color numbers and viewing angles are also factors that result in different prices. Understanding the panel technology behind the screen can let you strike a balance between your budget and needs.
The screen panel display can be roughly divided into two categories: Liquid crystal screen (LCD) category (TN, VA, and IPS display technology) and self-luminous category (AMOLED display).
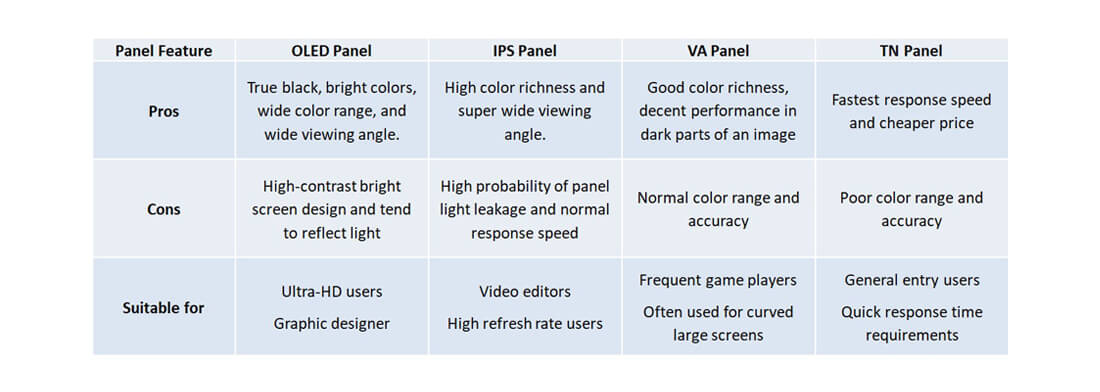
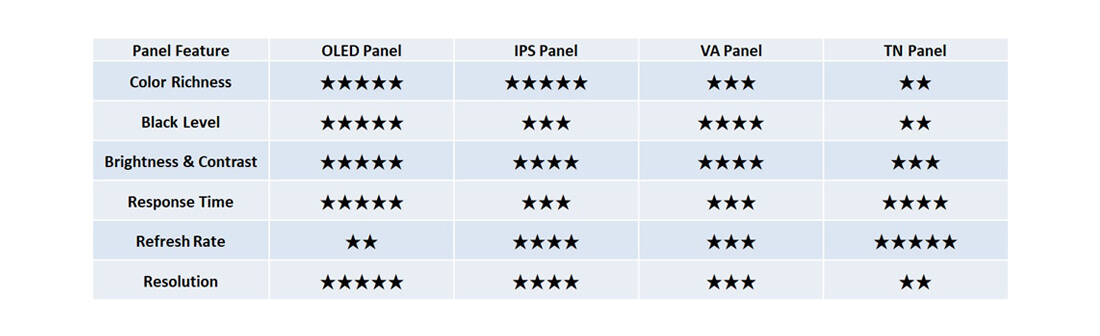
TN Panel
Commonly used in word-processing laptops, TN offers the advantage of being inexpensive but uses the lowest number of colors (6bit), meaning that the number of colors that can be displayed by each pixel is 262,000; significantly lower compared to the 16.77 million offered by other high resolution screens. TN panels have a bright backlight, so the true black is displayed in a grayer color. In addition, the biggest problem of the TN panel is the low viewing angle, which leads to a visible color shift when looking from different viewing angles.

VA Panel
Commonly found in larger-sized gaming and curved screen displays, the VA panels offer better response speed and a higher refresh rates. Therefore, VA panels can display more images per unit of time, shortening the pause between animations, reducing afterimages and tearing, further offering a better gaming and visual experience. The VA panel has a larger color display number reaching 16.77 million 8bit as well as better contrast. When searching for a gaming screen of similar price range, a VA panel should be the better choice for you.

IPS Panel
Commonly used in content creator laptops or professional color screens, the biggest advantage of IPS panels is the high replication of screen color. In addition to most of the colors achieving 8bit, IPS panel screens can accurately display the colors of an image and has a very large viewing angle so there’s no visible color difference when viewed from different angles. It is ideal for creators and photographers. Its past shortcoming is its slow response speed, so it was less commonly used in gaming screens. However, its refresh rate and response time has been greatly improved in recent years. IPS panels are now commonly used in gaming laptops with a refresh rate of 144Hz or higher. Different brands may adopt different names for this technology.

4K AMOLED Panel
Commonly found in high-definition high-end laptops or high-class OLED TVs, and not belonging to the LCD category (TN, VA, and IPS), an AMOLED screen with an active light-emitting panel is able to display the most vivid colors. AMOLED panels not only wield 10-bit color and over 1.07 billion colors, they are also certified as VESA DisplayHDR True Black, allowing for up to 100X deeper black levels and a greater dynamic range. The proportion of harmful blue light is 60% lower than that of ordinary LCD screens. In addition to having the response time of fewer than 0.5 milliseconds, it has the widest viewing angle compared to all previously mentioned display panels. There will be no difference in color from different viewing angles. Generally speaking, AMOLED screens are only used in high-end TVs. GIGABYTE’s AERO 15 OLED is the ever first laptop to adopt an AMOLED screen display.

Step 3. Final key: color gamut
The color gamut represents the range of colors visible to the human eye on an output device. The wider the color gamut range is, the richer the screen colors are. Otherwise, no matter how high the resolution is or how powerful the graphics card is, the screen will still look gray, yellow, and dim. The common color gamut range of laptops is NTSC, and it is often represented by a percentage; the higher the percentage, the bigger the color range that can be displayed. The VA and IPS panels mentioned above can usually display 8bit colors with about 72% NTSC. The display color of 10bit can reach 94% NTSC, offering a richer color range.

Step 4. Precise and comprehensive color calibration
Displaying color-rich and beautiful images cannot automatically be deemed professional, especially for photographers or image editors who value color accuracy above all else. Nowadays, many laptops in the market feature PANTONE (an international standard color agency) certification, which states that the color of the panel is as accurate as that of the color palette. There are different levels of PANTONE certification and in the current market, only GIGABYTE’s mid- and high-end laptops have joined Xrite PANTONE’s factory program, executing panel-by-panel color calibration.

Conclusion: Your eyes are the windows to the soul. Take good care of them!
Selecting the right panels for your laptop is not difficult but it’s very important. With many of users facing screens for over 8 hours at a time, having a display screen which offers finer images and more accurate colors can provide a better online experience and assist with creating work with realistic and beautiful color tones. Components such as memory and storage can be expanded to meet users’ needs. However, when it comes to laptop screen displays, no remedies can be adopted. Master these screen-picking tips and treat yourself with a laptop that satisfies your image quality needs today!